
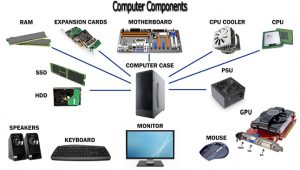
A purpose-built computer system that’s designed and customized to meet a specific customer’s needs. People build computers for gaming, video and photo editing, animation, web browsing, productivity needs and much more.
Make sure you, and anyone else involved in your operations use strong passwords. The longer and more complicated the password the safer. including smartphones, laptops, tablets, email accounts and computers.
Be wary of suspicious/unsolicited emails and links.
DO NOT OPEN a link when you do not know the source.
If it looks suspicious, don’t trust it.
Create data backups regularly, either on-site or off-site in a cloud provider. Don’t trust a single backup location. If the data is that important save it in triplicate if possible. Setup redundant backup systems for your important data.
Data recovery is the process of restoring data that has been lost, accidentally deleted, corrupted or made inaccessible, to a desktop, laptop, server or external storage system from a backup. There are two types of recoveries, logical data recovery and physical data recovery.
We are a group on computer nerds. Computers, tech and gaming are our passion. We offer quite a few services including but not limited to computer/laptop and console hardware repair services in Spanaway, WA and surrounding areas.
Pricing depends on the job, want your computer cleaned? decided you need it upgraded at the same time? Our prices are fair but vary by job so much that it’s better to just call and ask.
Basic Input Output System.
A BIOS is used for Loading the operating system.
The BIOS is stored in flash memory, which is located on the motherboard.
A boot sector, also known as a boot record, is a small, crucial section of a storage device, typically a hard drive or a solid-state drive (SSD), that plays a fundamental role in the computer’s startup process. It is the initial sector that is read by the computer’s firmware or BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) when the system is powered on or restarted.
The boot sector contains essential information and instructions that are necessary for the computer to load its operating system (OS). It typically includes:
Bootloader Code: This code instructs the computer on how to proceed with the boot process. It often provides options for selecting which operating system to load if there are multiple OS installations on the same system.
Partition Information: If the storage device is partitioned into multiple sections, the boot sector provides information about the structure and location of these partitions.
File System Information: The boot sector contains details about the file system used on the storage device. This information is crucial for the OS to access and manage the stored data.
Disk Signature: A unique identifier for the storage device, which helps the system differentiate between different drives.
When you turn on your computer, the firmware or BIOS first reads the boot sector from the storage device specified in the boot order. This sector’s instructions guide the system on how to proceed to load the OS into memory, enabling the computer to become operational.
A corrupted or damaged boot sector can lead to booting issues and prevent the operating system from loading. In such cases, repairs or recovery methods may be required to restore the functionality of the boot sector and the overall system.
CMOS stands for “Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor,” and it refers to a type of semiconductor technology used in the design and manufacturing of integrated circuits, including microprocessors, memory chips, and various digital logic circuits. CMOS technology has become a fundamental building block in modern electronics due to its low power consumption, high integration density, and compatibility with digital circuits.
In the context of computers, the term “CMOS” is often associated with the CMOS battery and the CMOS setup/utility, which play essential roles in the operation of a computer’s hardware and firmware:
CMOS Battery: A small battery, usually a coin-cell battery, that powers a chip called the CMOS chip or CMOS RAM. This battery ensures that certain essential system information, such as date, time, hardware configuration, and system settings, is retained even when the computer is powered off. If the CMOS battery becomes depleted or fails, the computer may lose this information, leading to issues such as incorrect date and time settings or BIOS configuration resets.
CMOS Setup/Utility: The CMOS setup, also known as the BIOS setup or UEFI setup, is a utility accessed during the computer’s boot process. It provides a user interface for configuring various hardware settings and parameters, such as boot order, system clock settings, CPU settings, memory timings, and more. Changes made in the CMOS setup are stored in the CMOS RAM and retained by the CMOS battery. The setup utility is used to customize the computer’s hardware behavior and functionality.
In summary, CMOS technology is a crucial aspect of modern electronics and plays a significant role in both the operation of integrated circuits and the configuration and maintenance of computer hardware settings. The CMOS battery and CMOS setup are specific components that are commonly associated with computer systems and their functionality.
Input Devices
1) Graphics Tablets 2) Cameras 3) Video Capture Hardware 4) Trackballs 5) Barcode reader 6) Digital camera 7) Gamepad 8) Joystick 9) Keyboard | 10) Microphone 11) MIDI keyboard 12) Mouse (pointing device) 13) Scanner 14) Webcam 15) Touchpads 16) Pen Input 17) Microphone 18) Electronic Whiteboard |
Output Devices
1.Monitor 2.Printers (all types) 3.Plotters 4.Projector 5.LCD Projection Panels 6.Computer Output Microfilm (COM) 7.Speaker(s) |
Both Input/Output
1.Modems 2.Network cards 3.Touch Screen 4. Headsets (Headset consists of Speakers and Microphone. Speaker act Output Device and Microphone act as Input device) 5. Facsimile (FAX) (It has scanner to scan the document and also have printer to Print the document) 6.Audio Cards / Sound Card |
At Who’s Your Data?, we prioritize the safety and security of your valuable information. Our comprehensive data security measures are designed to safeguard your digital assets from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. We offer robust protection against a wide range of malicious software, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware. Our expert team stays vigilant to the latest trends in cybercrime, ensuring that your systems are fortified against potential breaches. With a proactive approach, advanced encryption protocols, and vigilant monitoring, we create a shield of defense around your data, ensuring uninterrupted operations and peace of mind. Trust us to be your partner in safeguarding your digital world.
Data Security: Data security refers to the practice of safeguarding digital information and preventing unauthorized access, modification, or disclosure. It encompasses a range of measures and protocols designed to protect sensitive data from theft, breaches, or cyberattacks. Effective data security involves encryption, access controls, regular backups, network monitoring, and adherence to best practices to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
Virus: A virus is a type of malicious software that attaches itself to legitimate programs or files and replicates when those programs or files are executed. Viruses can spread rapidly and cause harm by corrupting or destroying data, disrupting system operations, and compromising the security of a computer or network.
Types of Viruses and Vulnerabilities:
Mitigation Strategies:
Difference Between Malware and Spyware: Malware is a broader term that encompasses various types of malicious software, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware. Spyware, on the other hand, is a specific type of malware designed to collect information from a device without the user’s knowledge. It can monitor online activities, track keystrokes, capture sensitive data, and transmit it to malicious actors. While spyware is a subset of malware, not all malware is spyware.
Customer Spotlight
Reseller Programs
Terms of Service
© 2022 Who’s Your Data? llc